The EDI 856 Document Type Explained

In the fast-paced world of modern commerce, being on top of your game means knowing exactly where your products are at any given moment.
If you act as a middleman, you don’t have to deal with the hassle of managing inventory yourself. But it does mean you need to constantly exchange information between your trading partners—and that can get complicated.
In an era where shoppers expect hassle-free delivery services and efficient fulfillment, shipment tracking is more important than ever.
That’s where electronic data interchange (EDI) comes in. EDI solutions allow businesses to electronically communicate information quickly and accurately throughout their supply chain.
There are multiple types of EDI documents, but one of the most important in eCommerce is advance ship notices, known as the EDI 856.
Let’s look at what EDI 856 is and how you can simplify it with the right platform.
What Is an EDI 856?

An EDI 856 advance shipment notice is a type of electronic document that notifies a recipient about the details of a shipment before it arrives.
While it’s used across sectors, it’s particularly important in the retail and automotive industries, where the timing and accuracy of information are critical for just-in-time production and inventory management.
Some of the reasons many major retailers and their suppliers use EDI 856 advance ship notices include:
Efficient communication: Communicate the data and details of a shipment, which reduces the time and potential for errors associated with manual data entry.
Better preparation: Helps partners and their facilities anticipate a shipment’s arrival, which facilitates smoother unloading, inventory management, and distribution processes.
Standardization: Adheres to EDI formats and standards, including those specified by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), thereby ensuring that it’s understood across the supply chain.
How Does EDI 856 Work?
The EDI 856 document plays a vital role in alerting a receiving party to the specifics of a shipment before it reaches the trading partner's facility or distribution center.
Here's a breakdown of how the EDI 856 process unfolds:
1. Initiation
Say, for example, a tech eCommerce company wants to order models of a new smartphone from one of their suppliers.
Depending on the order, the eCommerce company may send a purchase order (EDI 850), a planning schedule (EDI 830), or a shipping schedule (EDI 862).
The process begins once the supplier has established that they can meet the trading partner’s requirements, whereafter they’ll start preparing their shipment.
2. Creation of EDI 856
Before sending the smartphones, the supplier will generate an EDI 856 document that adheres to the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) standards.
This advanced shipment notice (ASN) includes comprehensive details, such as:
- Carrier information
- Tracking information
- Shipment information
- Item details
3. Transmission to trading partner
The EDI 856 is then electronically communicated to the partner.
In this case, the smartphone supplier will send the EDI 856 to the tech eCommerce platform.
This ensures that the trading partner is aware of the incoming shipment and its specifics, allowing them to prepare their facility or distribution center.
4. Receiving and acknowledgement
Upon receiving the EDI 856, the trading partner's system processes the information.
They then send back an EDI 997 Functional Acknowledgement to the supplier, confirming the successful receipt of the ASN.
This step verifies that the shipment information has been communicated effectively between the partners.
5. Preparation at partner's facility
With the advance ship notice, the partner can organize their operations to accommodate the incoming shipment.
This might involve arranging space in their warehouse, readying transportation equipment, scheduling labor on their ERP system, and preparing for inventory processing.
The Components of an EDI Advance Shipping Notice
Advance shipping notices go into various levels of detail about a shipment, offering as little as the tracking number or as much as including information for the barcode labels on each product.
An EDI 856 typically includes:
Partner information: Identifies the recipient of the goods and ensures the shipment meets the specific trading partner’s requirements.
Purchase order number: Links the shipment to a purchase order, allowing for precise tracking and inventory management.
Carrier information: Offers details on the transportation used, which is essential for tracking the shipment and understanding the logistics involved.
Shipping information and tracking information: Provides details about the shipment, including tracking numbers and physical characteristics, ensuring the trading partner can prepare for its arrival.
Advanced shipping notice (ASN): The core of the EDI 856, this advance ship notice includes information on the items shipped, respective quantities, packaging structure, and item tracking details, all formatted according to EDI ASN standards.
An example of an EDI 856
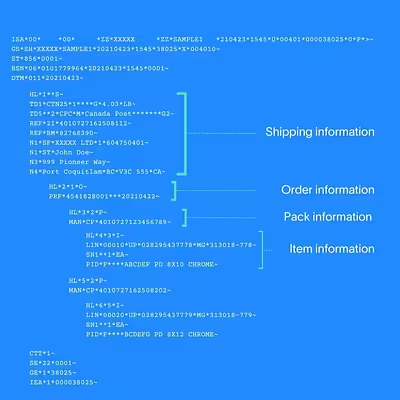
An EDI 856 might look like gibberish; however, each segment is structured to convey information about shipments in a standardized format that electronic systems can process.
In the above example, the EDI 856 document is broken down into sections that each serve a unique purpose:
Headers: The ISA segment is the start of the interchange and includes authorization information and security details. The GS segment provides group information, including the sender's and one or more receivers’ identification codes, and the date that the document was created.
Shipping information: This section includes information such as the transportation method and carrier details. It typically includes the carrier's name, equipment used, and other transportation-related details.
Order information: This part of the EDI 856 informs the receiver about which specific orders are included in the shipment. It references the purchase order numbers and can provide additional information relating to the order date and destination.
Packing information: Here, the document details how the items in the shipment are packed. It could specify the packaging material, how many items are in each package, and the order of the packages within the shipment.
Item description: This provides a list of the specific items being shipped. It includes item identifiers such as SKU numbers, detailed descriptions, and quantities.
Unlock Effortless EDI 856 Integration with Spark Shipping
As a retailer or dropshipper, managing the flow of goods can be time-consuming. But more importantly, managing them without a hitch is crucial in today’s fast-paced world. Spark Shippers is here to make that happen.
With Spark Shipping, you can automatically pull fulfillment information from the EDI 856 Advance Shipping Notice document and convey information to your customers. Say goodbye to manual data entry and hello to automated order fulfillment.
With Spark Shipping, implementing and automating EDI for your eCommerce store is easier than ever. Get in touch with us today!
Popular Posts
Posts by Topic
- Dropshipping (10)
- Dropshipping Automation (7)
- Dropship Suppliers (4)
- Amazon Seller Central (3)
- EDI (3)
- Pricing Strategy (3)
- Automotive Dropshipping (2)
- Conversion Rate Optimization (2)
- Dropshipping Products (2)
- Order Management (2)
- Shipping (2)
- Vendor Product Catalog (2)
- AI Dropshipping (1)
- Dean Soto (1)
- Feature Announcement (1)
- Online Empire Academy (1)
- Product Optimization (1)
- Walmart Marketplace (1)
- referral marketing (1)